How to setup an NGINX Ingress with cert-manager using Helmfile

In this blog, we will explain how to set up your NGINX Ingress with a TLS/SSL certificate using Helmfile.
The traditional methods, involve multiple steps and manual configurations, can be time-consuming and error-prone. for this demo, we are using the domains grafana-ai.takemetoprod.com and Nginx as load balancers.
Note: SSL & TLS are the same. SSL is the old name. TLS is the updated version of SSL. Don't get confused 🙂
Before starting a project let’s understand a few topics
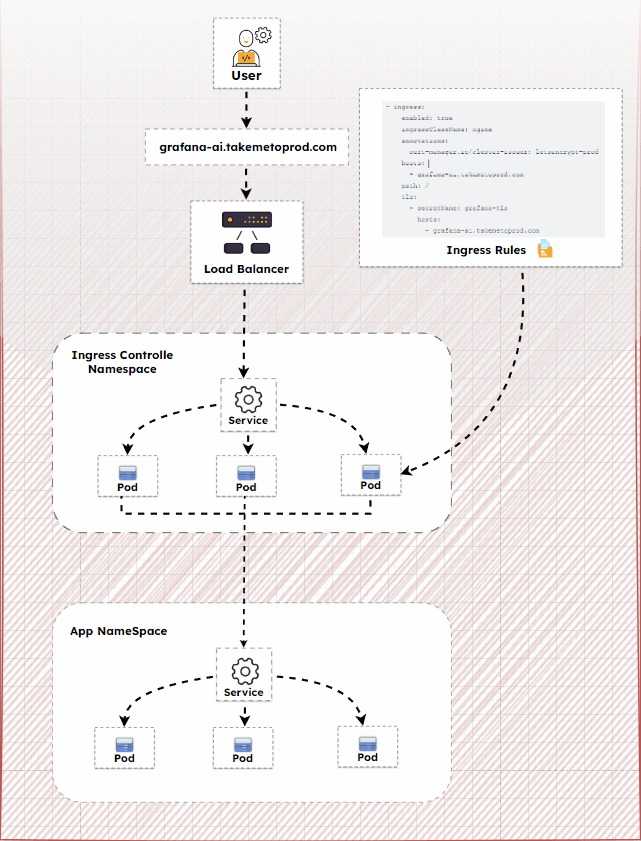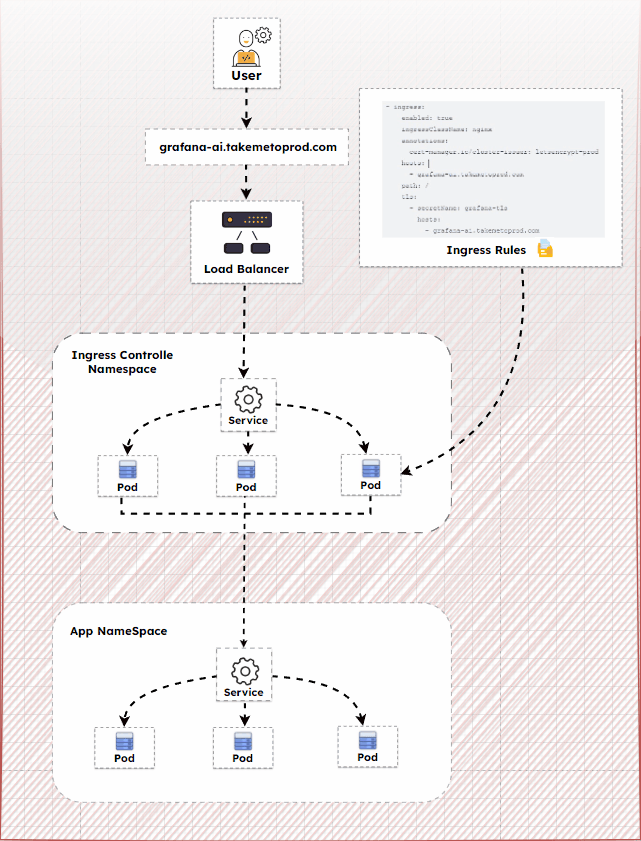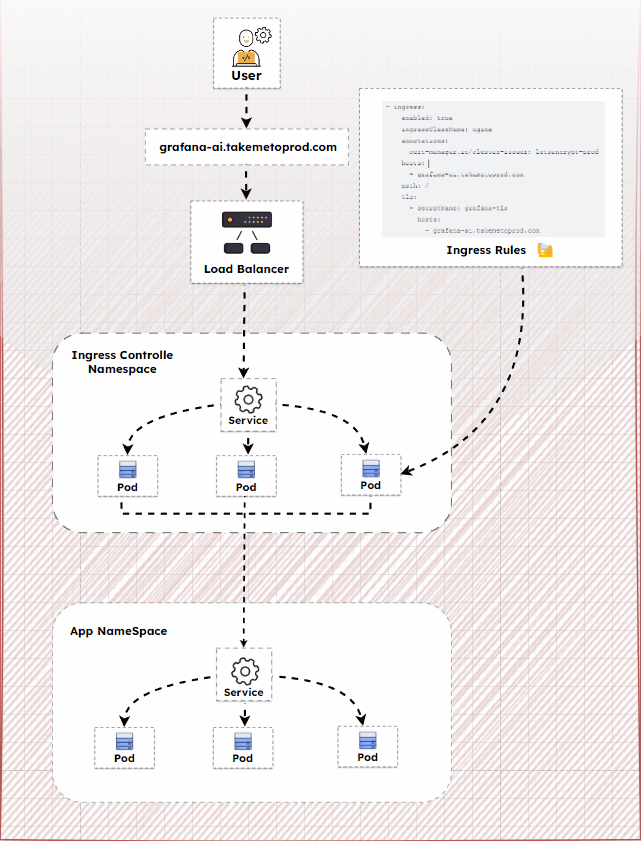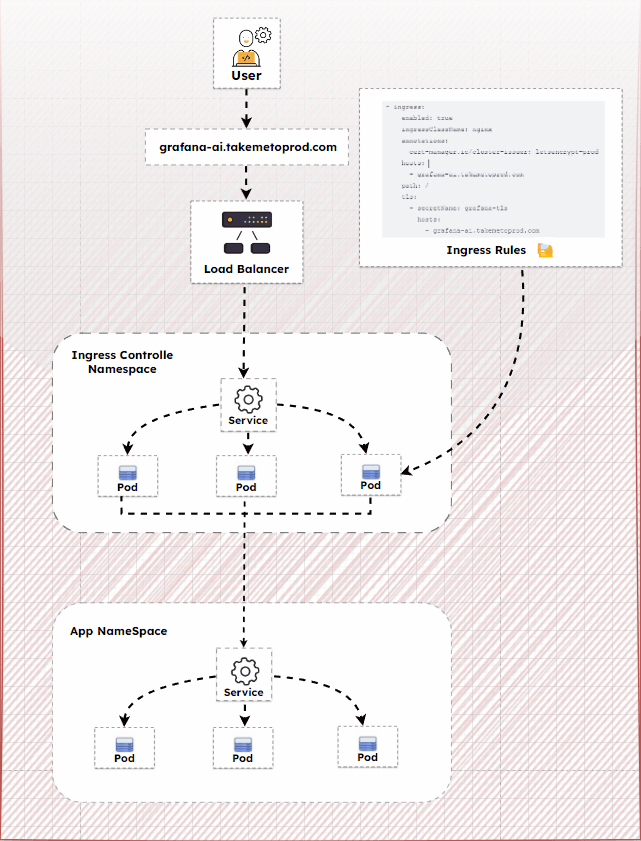
How Does Ingress Work?
NGINX Ingress Controller is an ingress controller that uses NGINX to manage ingress resources in a Kubernetes cluster. Ingress is a native Kubernetes resource like pods, deployments, etc. Using ingress, you can maintain the DNS routing configurations.
The ingress controller does the actual routing by reading the routing rules from ingress objects stored in ETCD. NGINX Ingress Controller provides HTTP and HTTPS routing to services based on URL paths and hostnames. You will need to configure NGINX Ingress to handle traffic and route it to your services.
The following diagram shows the high-level ingress workflow.
What are SSL/TLS Certificates and How Does Ingress TLS/SSL Work?
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network. For this project, you'll need a TLS certificate to secure your ingress traffic.
we can get a TLS/SSL certificate in several ways. One option is to create self-signed certificates using your own Certificate Authority (CA), suitable for development environments where you can share the root CA with your team to ensure browser trust.
For production environments, purchasing SSL certificates from well-known and trusted certificate authorities is recommended.
Another convenient option is to use Let’s Encrypt, a non-profit trusted certificate authority that provides free TLS certificates. Keep in mind that all SSL certificates come with an expiry date and require rotation before they expire. For this practical, we will use Let’s Encrypt certificates.
The Nginx Ingress Controller automatically configures Nginx to handle SSL based on the Ingress resource. When you create or update an Ingress resource with TLS settings, the Ingress Controller updates its internal configuration.
In the Nginx configuration (nginx.conf), the Ingress Controller dynamically handles SSL certificates using Lua scripts. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- Nginx Configuration File (
nginx.conf): This file defines how Nginx operates, including how it handles SSL. - Lua Script for SSL: The
ssl_certificate_by_lua_blockdirective innginx.confallows Nginx to dynamically load SSL certificates using Lua scripts.
The following diagram shows the high-level ingress TLS workflow.
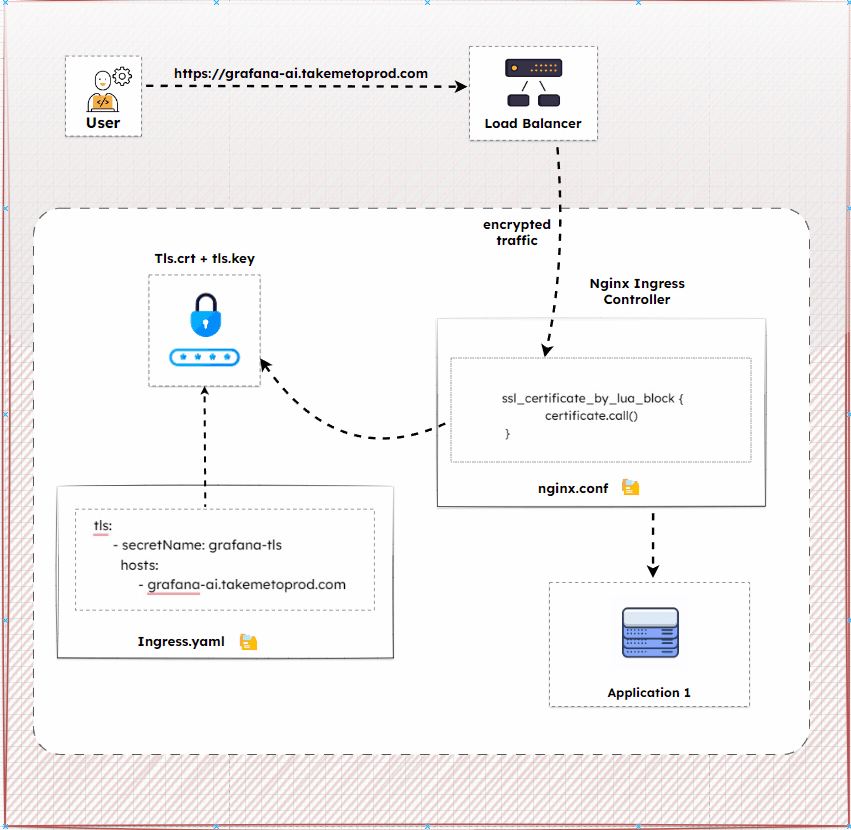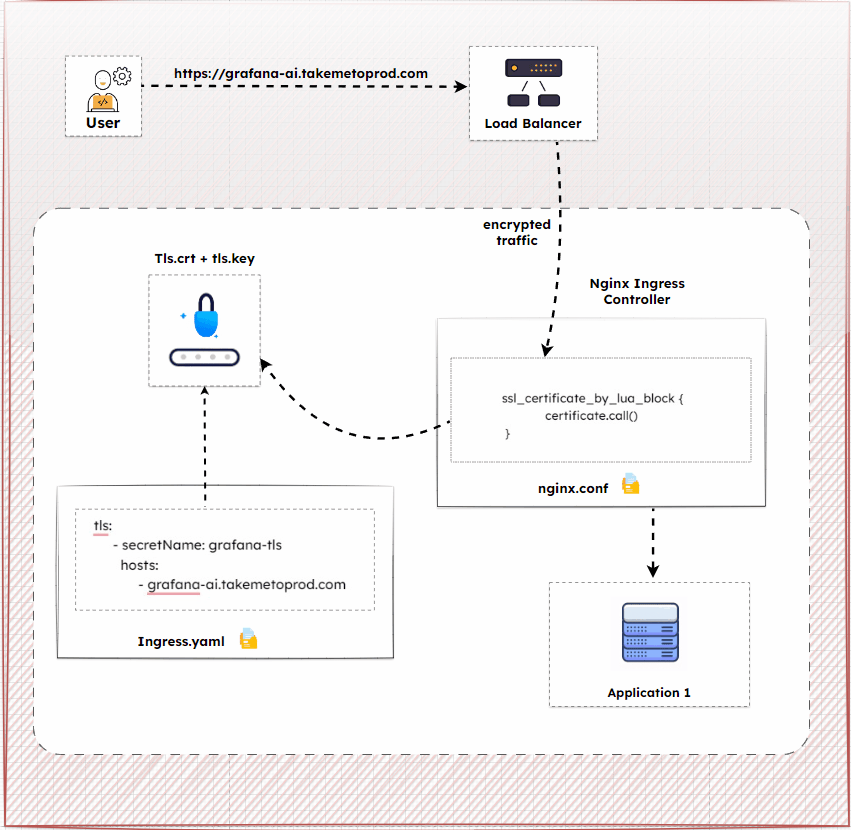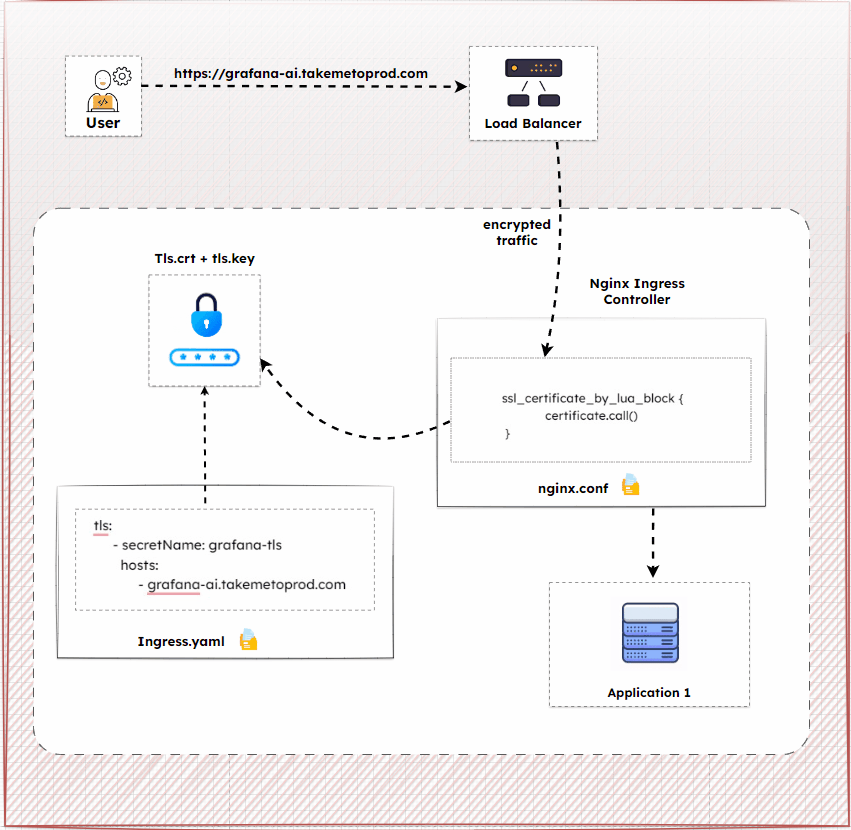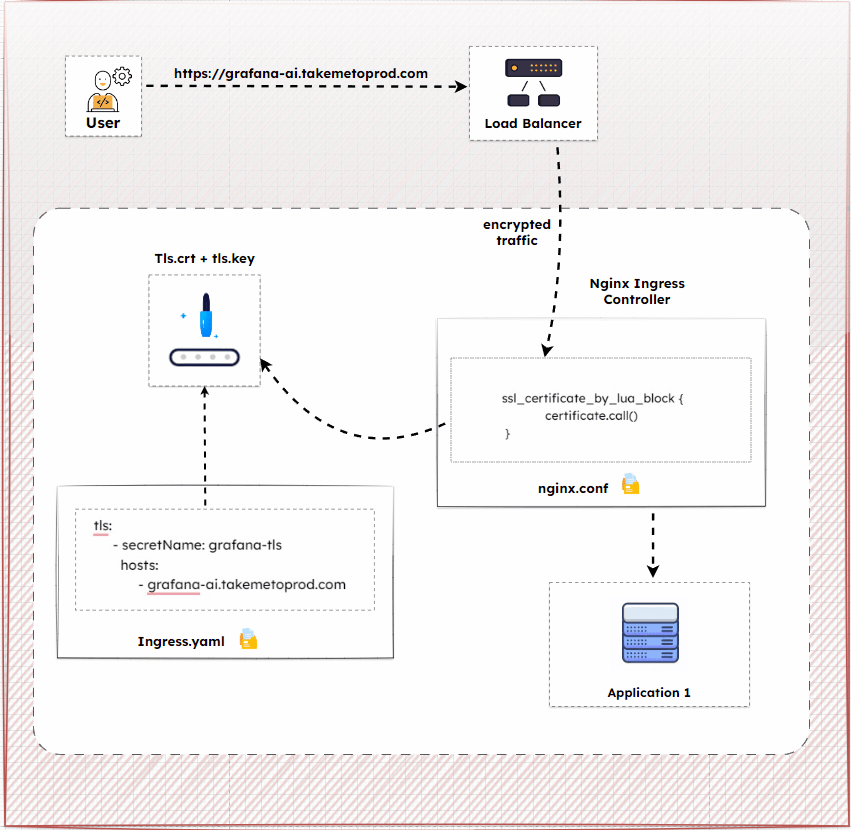
Let’s look a the steps in configuring TLS in ingress. we will use a grafana application to test our ingress TLS.
Step-by-Step Explanation
- Define Environments: Sets the default Kubernetes context to `KubeNine.
environments:
default:
kubeContext: KubeNine
- Add Helm Repositories: Adds the repositories for fetching Helm charts.
repositories:
- name: stable
url: https://charts.helm.sh/stable
- name: jetstack
url: https://charts.jetstack.io
- name: grafana
url: https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
- Install Nginx Ingress Controller: Install the Nginx ingress controller in the
Nginxnamespace with snippet annotations enabled.
releases:
- chart: ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx
namespace: nginx
name: nginx
version: ~4.10.0
values:
- controller:
allowSnippetAnnotations: true
- Install Cert-Manager: Deploys cert-manager in the
cert-managernamespace with necessary DNS challenge arguments.
- name: cert-manager
namespace: cert-manager
createNamespace: true
chart: jetstack/cert-manager
version: ~1.14.0
set:
- name: installCRDs
value: true
values:
- extraArgs:
- --dns01-recursive-nameservers-only
- --dns01-recursive-nameservers=8.8.8.8:53,1.1.1.1:53
- Install Grafana: Deploys Grafana with ingress enabled, configured for TLS using Let's Encrypt.
- name: grafana
namespace: prudvi
chart: grafana/grafana
values:
- ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
hosts:
- grafana-ai.takemetoprod.com
path: /
tls:
- secretName: grafana-tls
hosts:
- grafana-ai.takemetoprod.com
- Post-Init Job: includes a placeholder for post-initialization tasks, such as applying
ClusterIssuer.
- name: post-init
namespace: cert-manager
chart: ./post-init
Ensure that the post-init chart contains the following manifest file for the ClusterIssuer:
# post-init/cluster-issuer.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: PleaseEnterYourMailID@kubenine.com
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
Applying the Helmfile:
To deploy these configurations, run the following command:
helmfile sync
Conclusion
Using Helmfile to manage Kubernetes deployments allows you to define, version, and automate your Helm charts clearly and consistently. This setup ensures your ingress controller, certificate manager, and applications are configured correctly with TLS, providing a secure and reliable setup.
Learn how nginx-image-resizer Simplifies Image Handling for Your Web Apps : https://www.kubeblogs.com/how-nginx-image-resizer-simplifies-image-handling-for-your-web-apps/

