Table of Contents
Introduction
Running GPU workloads on Amazon ECS requires careful planning and specific configurations that differ from standard CPU-based deployments. Organizations need GPU computing for machine learning training, inference workloads, video processing, and scientific computing, but ECS GPU support comes with important limitations and requirements
ECS GPU support is only available through EC2 capacity providers, not Fargate. This means you must manage your own compute infrastructure, select appropriate GPU-enabled instance types, and configure the underlying AMI with proper drivers. The process involves setting up capacity providers with user data scripts, configuring task definitions with GPU resource requirements, and ensuring proper driver installation.
This guide covers the complete implementation process for running GPU workloads on ECS, including AMI selection, capacity provider configuration, and task definition setup.
Prerequisites and Limitations
ECS GPU Support Scope: - Only available through EC2 capacity providers - Fargate does not support GPU workloads - Requires GPU-enabled instance types (p3, p4, g4, g5 series) - AMI must include NVIDIA drivers and Docker GPU runtime
Instance Type Requirements:
- p3.2xlarge and larger for Tesla V100 GPUs
- p4d.24xlarge for A100 GPUs
- g4dn.xlarge and larger for T4 GPUs
- g5.xlarge and larger for A10G GPUs
Architecture Overview
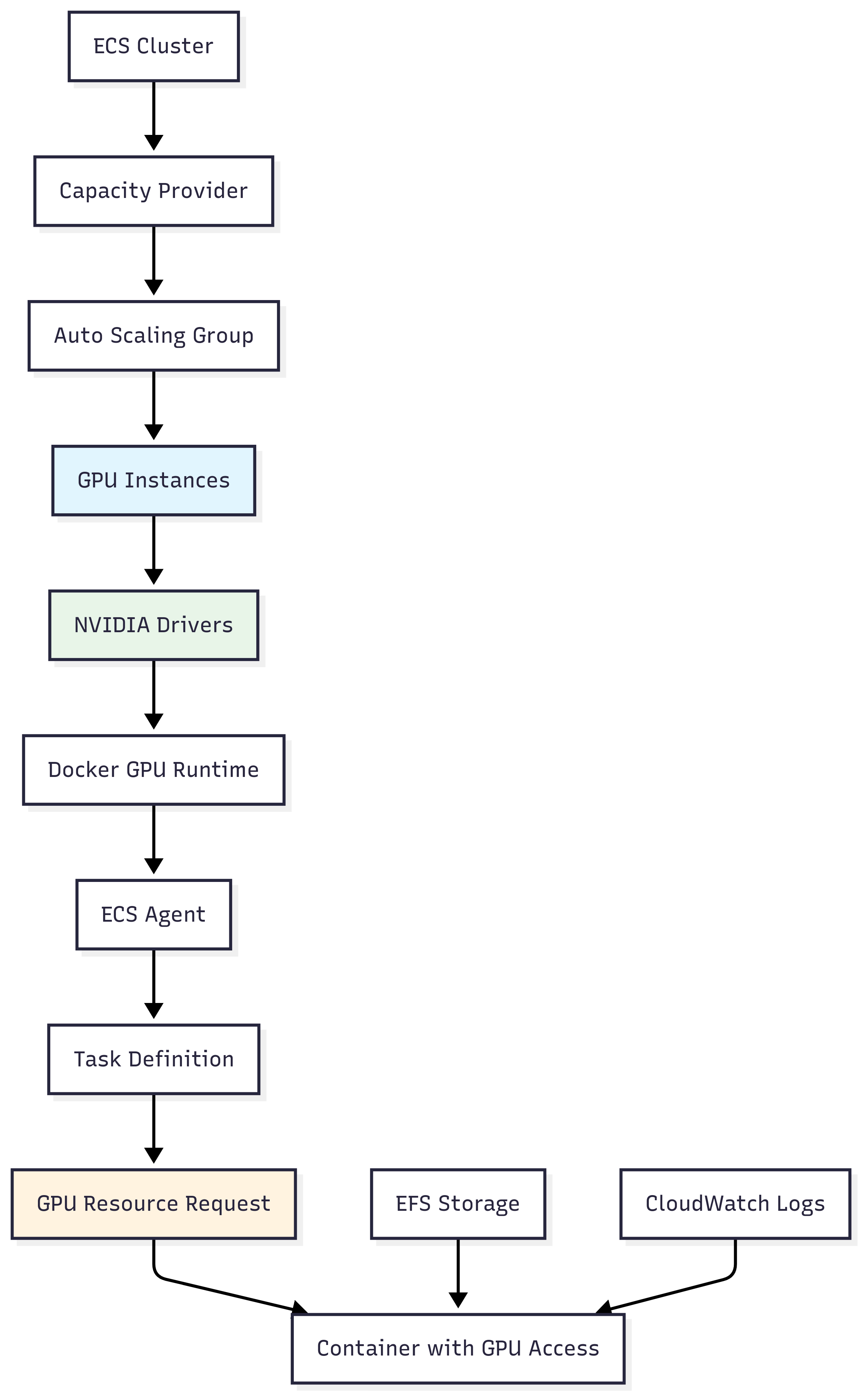
Key Configuration Points
Critical GPU Settings:
- User Data Script: Must include ECS_ENABLE_GPU_SUPPORT=true in /etc/ecs/ecs.config.
- Task Definition: Use resource_requirements with type = "GPU" and value = "1."
- Capacity Provider: Service must use the GPU capacity provider strategy. 4. AMI Selection: Deep Learning AMI includes pre-configured NVIDIA drivers
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Select the Right AMI
Choose an AMI that includes NVIDIA drivers and Docker GPU runtime support:
Option 1: AWS Deep Learning AMI—pre-configured with CUDA, cuDNN, Docker, and NVIDIA Container Toolkit—includes ECS-optimized agent and supports multiple CUDA versions. - Available in most regions
Option 2: ECS-Optimized AMI with GPU Support - Base ECS AMI with GPU drivers added - Lighter weight than Deep Learning AMI - Requires manual driver installation
Option 3: Custom AMI—Build from scratch with specific driver versions. - Maximum control over software stack - Highest maintenance overhead
Step 2: Configure Capacity Provider
# Data source for GPU instance types
data "aws_ec2_instance_type_offerings" "gpu_instances" {
filter {
name = "instance-type"
values = ["p3.2xlarge", "p4d.24xlarge", "g4dn.xlarge", "g5.xlarge"]
}
filter {
name = "location-type"
values = ["availability-zone"]
}
}
# Launch template with GPU support
resource "aws_launch_template" "gpu_ecs" {
name_prefix = "gpu-ecs-template"
image_id = "ami-0c02fb55956c7d316" # Deep Learning AMI
instance_type = "p3.2xlarge"
user_data = base64encode(<<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
# CRITICAL: Enable GPU support in ECS config
cat > /etc/ecs/ecs.config <<ECS_CONFIG
ECS_ENABLE_GPU_SUPPORT=true
ECS_ENABLE_TASK_ENI=true
ECS_ENABLE_TASK_IAM_ROLE=true
ECS_ENABLE_CONTAINER_METADATA=true
ECS_ENABLE_TASK_METADATA=true
ECS_ENABLE_SPOT_INSTANCE_DRAINING=true
ECS_ENABLE_AWSLOGS_EXECUTION_ROLE_OVERRIDE=true
ECS_AWSVPC_BLOCK_IMDS=true
ECS_ENABLE_TASK_CPU_LIMIT=true
ECS_ENABLE_TASK_MEMORY_LIMIT=true
ECS_CONFIG
# NVIDIA toolkit is pre-installed on the selected AMI
EOF
)
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.ecs_gpu.id]
iam_instance_profile {
name = aws_iam_instance_profile.ecs_instance.name
}
}
# Auto Scaling Group
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "gpu_ecs" {
name = "gpu-ecs-asg"
desired_capacity = 1
max_size = 10
min_size = 1
target_group_arns = []
vpc_zone_identifier = var.subnet_ids
launch_template {
id = aws_launch_template.gpu_ecs.id
version = "$Latest"
}
tag {
key = "Name"
value = "gpu-ecs-instance"
propagate_at_launch = true
}
tag {
key = "ECSCluster"
value = aws_ecs_cluster.gpu.name
propagate_at_launch = true
}
}
# ECS Capacity Provider
resource "aws_ecs_capacity_provider" "gpu" {
name = "gpu-capacity-provider"
auto_scaling_group_provider {
auto_scaling_group_arn = aws_autoscaling_group.gpu_ecs.arn
managed_termination_protection = "DISABLED"
managed_scaling {
maximum_scaling_step_size = 1000
minimum_scaling_step_size = 1
status = "ENABLED"
target_capacity = 100
}
}
}
# ECS Cluster
resource "aws_ecs_cluster" "gpu" {
name = "gpu-cluster"
capacity_providers = [aws_ecs_capacity_provider.gpu.name]
default_capacity_provider_strategy {
capacity_provider = aws_ecs_capacity_provider.gpu.name
weight = 1
}
}Step 3: Configure Task Definition and Service
Create a task definition with GPU resources and a service that uses the capacity provider:
# Task Definition with GPU resources
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "gpu_workload" {
family = "gpu-workload"
requires_compatibilities = ["EC2"]
network_mode = "awsvpc"
cpu = 2048
memory = 8192
execution_role_arn = aws_iam_role.task_execution.arn
task_role_arn = aws_iam_role.task_role.arn
container_definitions = jsonencode([
{
name = "gpu-container"
image = "nvidia/cuda:11.8-base-ubuntu20.04"
command = ["/bin/bash", "-c", "nvidia-smi && echo 'GPU workload started' && sleep 3600"]
essential = true
log_configuration = {
log_driver = "awslogs"
options = {
awslogs-group = aws_cloudwatch_log_group.gpu_workload.name
awslogs-region = data.aws_region.current.name
awslogs-stream-prefix = "gpu"
}
}
port_mappings = [
{
container_port = 8080
protocol = "tcp"
}
]
environment = [
{
name = "NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
value = "all"
},
{
name = "NVIDIA_DRIVER_CAPABILITIES"
value = "compute,utility"
}
]
# KEY: GPU resource requirement
resource_requirements = [
{
type = "GPU"
value = "1"
}
]
}
])
}
# ECS Service using the capacity provider
resource "aws_ecs_service" "gpu_service" {
name = "gpu-service"
cluster = aws_ecs_cluster.gpu.id
task_definition = aws_ecs_task_definition.gpu_workload.arn
desired_count = 1
# KEY: Use the GPU capacity provider
capacity_provider_strategy {
capacity_provider = aws_ecs_capacity_provider.gpu.name
weight = 1
}
network_configuration {
subnets = var.subnet_ids
security_groups = [aws_security_group.ecs_gpu.id]
assign_public_ip = true
}
}
# CloudWatch Log Group
resource "aws_cloudwatch_log_group" "gpu_workload" {
name = "/ecs/gpu-cluster/gpu-workload"
retention_in_days = 7
}
# Data source for current region
data "aws_region" "current" {}
#Variables
variable "subnet_ids" {
description = "Subnet IDs for ECS instances"
type = list(string)
}
variable "vpc_id" {
description = "VPC ID for ECS cluster"
type = string
}Step 4: Deploy and Monitor
Deployment Commands:
# Initialize and deploy with Terraform
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply# Monitor GPU usage
aws ssm send-command \
--instance-ids i-1234567890abcdef0 \
--document-name "AWS-RunShellScript" \
--parameters 'commands=["nvidia-smi"]'# Check ECS service status
aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster gpu-cluster \
--services gpu-service
Monitoring GPU Usage:
# Check GPU utilization on instances
aws ssm send-command \
--instance-ids i-1234567890abcdef0 \
--document-name "AWS-RunShellScript" \
--parameters 'commands=["nvidia-smi"]'# Monitor ECS service
aws ecs describe-services \
--cluster ecs-gpu-cluster-gpu-cluster \
--services gpu-serviceBest Practices
- Instance Selection: Choose GPU instances based on workload requirements and budget constraints
- Driver Management: Use Deep Learning AMI for production workloads to ensure driver compatibility
- Resource Planning: Monitor GPU utilization and scale capacity providers accordingly
- Cost Optimization: Use Spot instances for non-critical GPU workloads
- Security: Implement proper IAM roles and security groups for GPU instances
Conclusion
Running GPU workloads on ECS requires careful infrastructure planning and configuration. The key components include selecting the right AMI with GPU drivers, configuring capacity providers with proper user data scripts, and defining tasks with GPU resource requirements.
Start with a small GPU cluster using Deep Learning AMI to validate your setup, then scale based on workload requirements. Monitor GPU utilization and costs to optimize your infrastructure over time.
KubeNine Consulting helps organizations implement GPU workloads on ECS and other container platforms. Visit KubeNine—DevOps and Cloud Experts for assistance with your GPU infrastructure implementation.