Table of Contents
Civo Kubernetes clusters do not have a private only load balancer. So if you have a need to create a load balancer that is accessible only in the private network then you can use a custom firewall rule. By default, Civo creates load balancers with both public and private IP addresses.
This guide walks you through creating an internal load balancer in Civo by combining Civo's load balancer service type with network firewall rules.
Creating an Internal Load Balancer with Firewall Rules
Civo doesn't natively support an "internal" load balancer type, but you can achieve this behavior by creating a standard LoadBalancer service and attaching a firewall that blocks all inbound internet traffic.
Step 1: Create a Firewall Rule
First, create a firewall in your Civo account. By default no rules will be added on firewall and hence no incoming traffic will be allowed.
# Using Civo CLI
$ civo firewall create civocli_demo
Created a firewall called civocli_demo with ID ab2a25d7-edd4-4ecd-95c4-58cb6bc402deStep 2: Deploy a LoadBalancer Service with Firewall Annotation
Create your Kubernetes service with the kubernetes.civo.com/firewall-id annotation:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: internal-api-service
annotations:
kubernetes.civo.com/firewall-id: "ab2a25d7-edd4-4ecd-95c4-58cb6bc402de" # firewall id obtained earlier
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: my-api
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
sessionAffinity: ClientIP
Deploy this service to your cluster:
kubectl apply -f internal-lb-service.yaml
Step 3: Verify the Load Balancer Configuration
Check that your service received an external IP:
kubectl get svc internal-api-service -w
You should see output similar to:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
internal-api-service LoadBalancer 10.43.158.20 103.151.92.45 80:30847/TCP 2mThe load balancer now has a IP address, but it's protected by the firewall that blocks public internet access.
The important point here is that this load balancer also has an Internal IP address that is not visible on the kubectl cli. To see view the private IP go to Load Balancers section on your civo dashboard. You can get the private IP there.
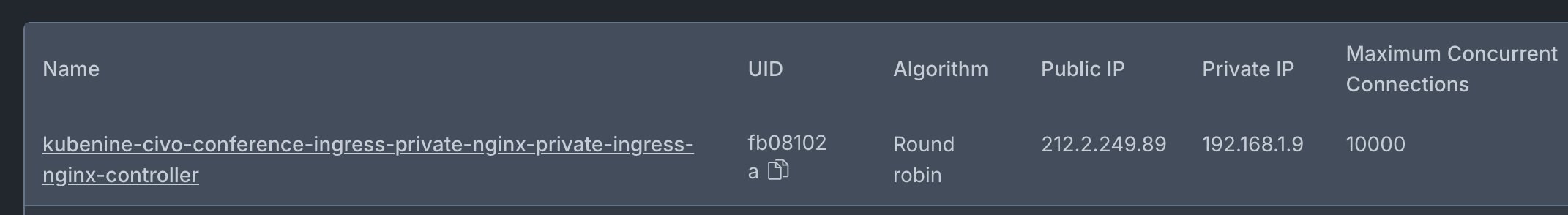
Step 4: Test Internal Access
From within your cluster or a machine on the private network, verify the load balancer is accessible:
# From inside a pod
kubectl run test-pod --image=curlimages/curl -it --rm -- \
curl http://192.168.1.9
Step 5: Verify Public Access is Blocked
From outside your cluster (the public internet), attempt to access the load balancer:
# This should timeout or be refused
curl -v http://103.151.92.45 --connect-timeout 5
The connection should fail, confirming the firewall is blocking public traffic.
Conclusion
Creating an internal load balancer in Civo Kubernetes involves attaching a restrictive firewall to a standard LoadBalancer service and using the Private IP provided by the load balancer. This approach provides security by blocking public internet access while maintaining providing full access for internal VPC traffic.