Table of Contents
Introduction
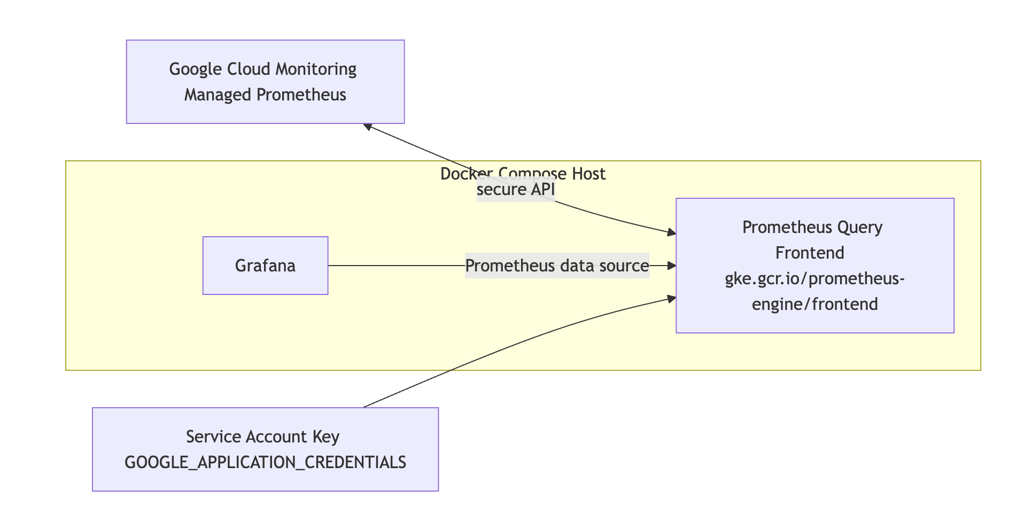
Google Cloud Managed Prometheus (GMP) lets you store and query Prometheus metrics in Google Cloud Monitoring without running your own Prometheus servers. If you want a familiar Prometheus-style experience in Grafana, you can run the Prometheus query frontend container locally and point Grafana’s Prometheus data source at it. The query frontend authenticates to Google Cloud using a service account and translates PromQL queries to Google Cloud Monitoring API calls.
This guide shows a minimal, production-friendly setup using Docker Compose. You’ll create a least-privilege service account, run the managed Prometheus query frontend, and connect Grafana to it. The end result: you can explore your Google Cloud metrics with PromQL in Grafana, without operating Prometheus storage yourself.
Prerequisites
- Docker and Docker Compose installed
- Google Cloud project ID where your GMP metrics live
- gcloud CLI authenticated with permissions to create service accounts and IAM bindings
Create a service account and key (least privilege)
Replace PROJECT_ID with your Google Cloud project ID.
gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
# Create a dedicated service account for Grafana → GMP reads
gcloud iam service-accounts create grafana-gmp-reader \
--display-name="Grafana GMP Reader"
# Grant read-only access to metrics
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:grafana-gmp-reader@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/monitoring.viewer"
# Enable the Monitoring API if not already enabled
gcloud services enable monitoring.googleapis.com
# Create a JSON key (store securely!)
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create service-account-key.json \
--iam-account=grafana-gmp-reader@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.comSecurity notes:
- Prefer avoiding long-lived keys in production. If you’re running on GKE or GCE, use Workload Identity instead of keys. For hybrid/self-hosted, consider Workload Identity Federation.
- Scope permissions to only the projects you need. roles/monitoring.viewer is typically sufficient for read-only querying.
Docker Compose for Grafana and the Prometheus query frontend
Create a docker-compose.yaml with the following content. Replace YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID with your project and point the volume to your downloaded key file.
version: '3.8'
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: grafana
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER=admin
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=change-me
volumes:
- grafana-storage:/var/lib/grafana
restart: unless-stopped
prometheus:
image: gke.gcr.io/prometheus-engine/frontend:v0.15.3-gke.0
container_name: gmp-query-frontend
ports:
- "9090:9090"
environment:
- GMP_PROJECT=YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID
- GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=/etc/gcp/service-account-key.json
volumes:
- ./service-account-key.json:/etc/gcp/service-account-key.json:ro
command:
- "--web.listen-address=:9090"
- "--query.project-id=YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID"
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
grafana-storage:Bring the stack up:
docker compose up -dConfigure Grafana to use the Prometheus query frontend
- Open Grafana at <http://localhost:3000> (default user admin, password you set).
- Navigate to Connections → Data sources → Add data source → Prometheus.
- Set URL to <http://prometheus:9090> (the Docker Compose service name and port).
- Save & test.
Validate with a simple query
In Grafana Explore, select the Prometheus data source and try queries such as:
upIf you have GMP scraping configured in your project, you can also try common container metrics like:
container_cpu_usage_seconds_totalIf queries return no data, double-check:
- The project ID in Docker Compose flags and GMP_PROJECT
- The service account role (roles/monitoring.viewer)
- That Google Managed Prometheus is ingesting metrics in your project
Conclusion
With a lightweight Docker Compose setup, you can explore Google Cloud Managed Prometheus metrics in Grafana using standard PromQL—no Prometheus storage to manage. Keep credentials safe, prefer identity-based access over keys where possible, and consider provisioning for repeatable environments. From here, import or build dashboards targeting <http://prometheus:9090> and iterate on your observability views.