Table of Contents
Container security starts with protecting sensitive data during the build process. When secrets leak into Docker images, they become accessible to anyone with image access, creating significant security vulnerabilities. This guide provides practical techniques to prevent secrets from entering your Docker images.
Understanding the Problem
Secrets accidentally included in Docker images pose serious security risks. Once baked into an image layer, secrets remain accessible even if removed in subsequent layers due to Docker's layered filesystem architecture.
Docker Build Context
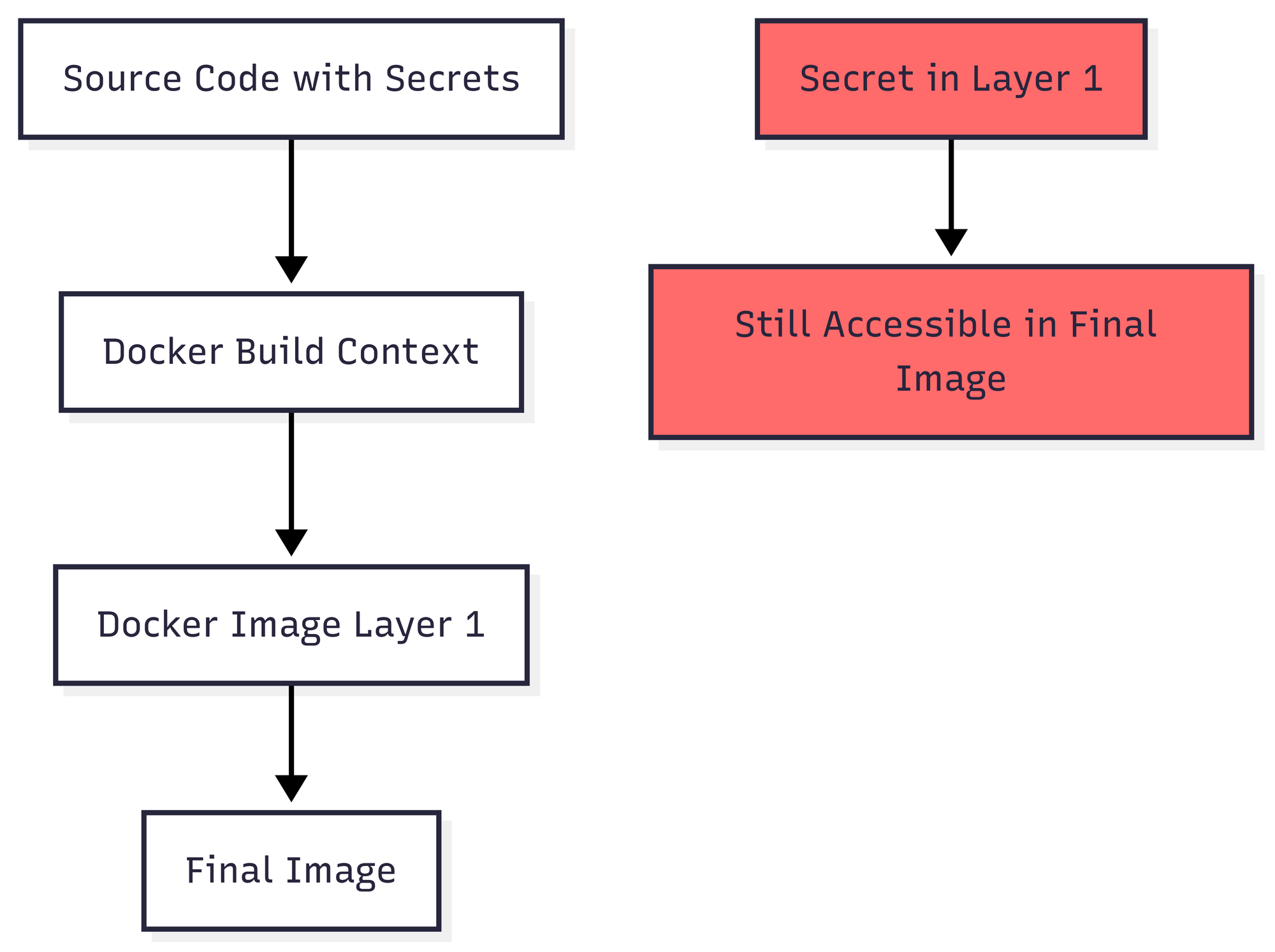
Common scenarios where secrets leak into images include:
- Configuration files containing API keys or database credentials
- Environment files (.env) with sensitive data
- SSH keys or certificates in the build context
- Temporary files created during build process
Using .dockerignore Effectively
The .dockerignore file serves as your first line of defense, preventing sensitive files from entering the Docker build context.
Basic .dockerignore Configuration
Create a comprehensive .dockerignore file in your project root that ignores all secret files:
# Environment files
.env
.env.*
*.env
# Secret directories
secrets/
keys/
certs/
*.key
*.pem
# Application logs
logs/
*.log
# Temporary files
tmp/
temp/
.cache/
# Version control
.git/
.gitignore
# Development tools
.vscode/
.idea/
Managing Environment Variables
Never include .env files in Docker images. Instead, use a layered approach:
# Project structure
project/
├── .env.example # Template with dummy values
├── .env # Local development (gitignored)
├── .env.production # Production secrets (never in repo)
├── .dockerignore # Excludes .env files
└── Dockerfile
Create a .env.example file as a template:
# .env.example
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:password@localhost:5432/dbname
API_KEY=your_api_key_here
JWT_SECRET=your_jwt_secret_here
Runtime Secret Injection
Implement patterns that inject secrets at container startup rather than build time.
E.g
- Use Secret in Kubernetes to mount environment variables at runtime
Advanced Security Patterns
Secret Scanning in CI/CD
Implement automated secret detection in your build pipeline:
# GitHub Actions example
name: Security Scan
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
secret-scan:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Run secret scan
uses: trufflesecurity/trufflehog@main
with:
path: ./
Image Scanning
Scan built images for accidentally included secrets:
# Using trivy
trivy image --security-checks secret your-app:latest
Conclusion
Protecting secrets in Docker images is easy, but people tend to miss the easy things.
Use a combination of following solutions to avoid leakage of secrets
- Use .dockerignore to prevent sensitive files from entering build context
- Never include .env files in images; inject environment variables at runtime
- Inject secrets at runtime.
- Automate secret scanning in CI/CD pipelines
- Monitor applications for accidental secret exposure
The investment in proper secret management pays dividends in security posture and compliance.